The Healthy Aging in Industrial Environment HAIE Project
The aim of the Healthy Aging in Industrial Environment HAIE project is to assess the influence of selected environmental risk factors and lifestyle upon the health and aging of population in an industrial region (Moravian-Silesian Region) and outside of this region (South Bohemian Region and Prague).
This project, which belongs among excellent projects, was created building upon current problems of the public health sector, and was supported within the Operational Programme Research, Development and Education of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic. The project is predominantly co-financed by the European Union, and is planned for the period from 2018 to 2022. Other follow-up projects are planned in the future, including international ones.
The aim of the research is to find relations among the environment, lifestyle, medical condition, quality of life and aging. Another significant aim of the project is building valuable cohorts for long-term prospective monitoring of health and other selected parameters in the observed population.
The applicability of results of this excellent research lies in their high potential to be used in medicine, as the basis for formulating recommendations and interventions pointed towards a better policy of protection and support of public health.
Apart from this, the HAIE project will provide support for excellent research, and bring about improvement of infrastructure of the existing research centres, development of research teams and their internationalization.
Methods
The basis of the project is foundation of cohorts for long-term monitoring of health:
- Cohort of middle-aged individuals (35 – 65 years)
- Cohort of mothers and their children from birth
- Cohort of adult runners
- Cohort of municipal police officers
The methods used within the project will include epidemiological studies, from the level of morbidity within the population and socioeconomic factors, up to molecular biological studies aimed at influencing genetic, epigenetic, and metabolic indicators of fertility and injury rates during physical activities.
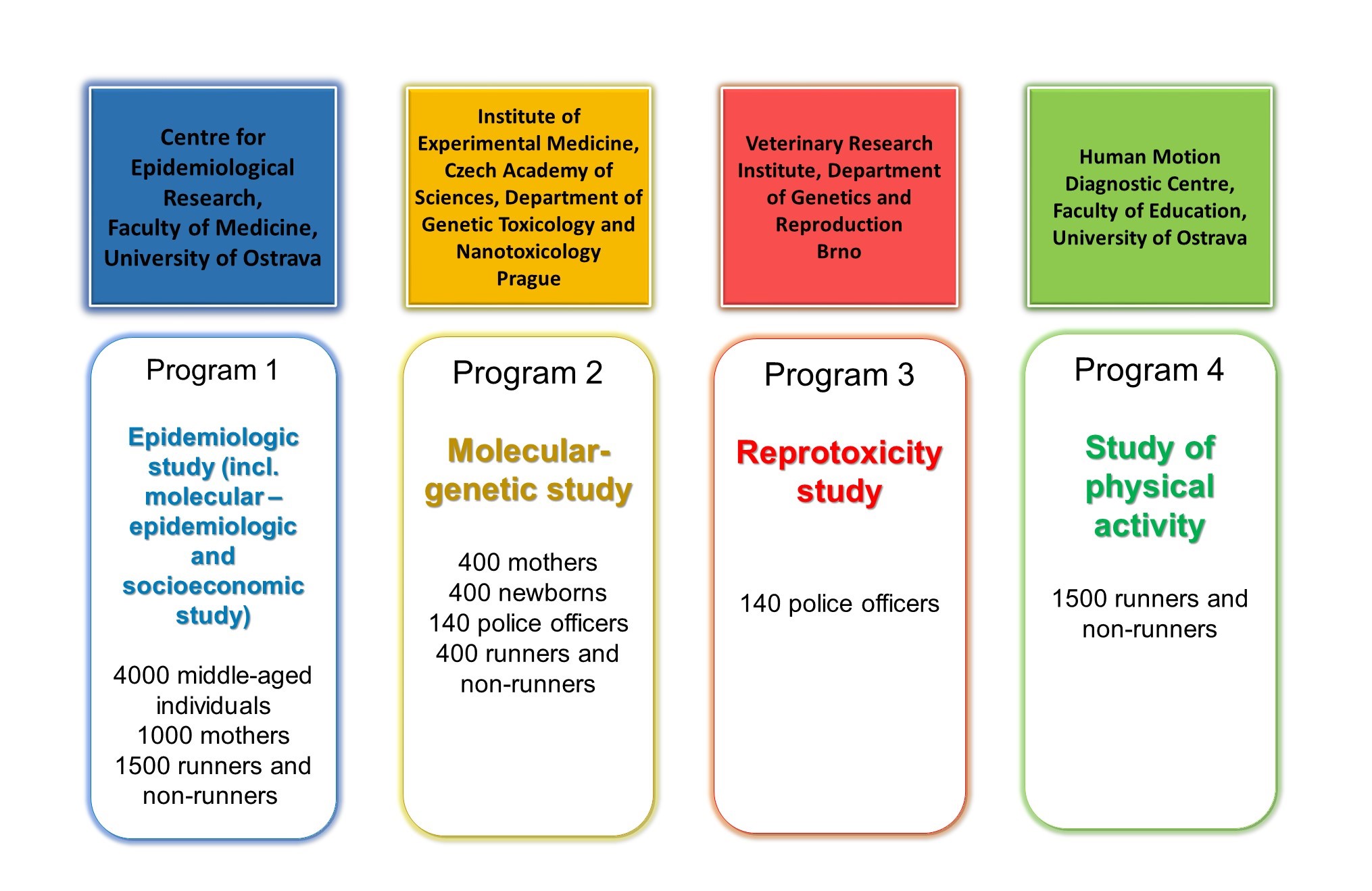
The HAIE project consists of four independent programmes, which mutually cooperate. These research programmes, realized by the research centres, are mutually interconnected with shared data from study participants and analyses, e.g. of the biological material, measured values of air quality, and information from common questionnaires.
Programme 1: Epidemiological (including molecular-epidemiological) and socioeconomic study of specific diseases and selected health indicators
Principle investigator: Faculty of Medicine, University of Ostrava, Centre for Epidemiological Research
The content of the epidemiological study is the research and evaluation of relations between exposition towards external environmental factors, factors of lifestyle, their impact upon health and aging in middle-aged individuals. Cohort studies and case control studies will be performed. Also the influence of the combination of exposition towards polluted air and lifestyle upon selected diseases (cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the respiratory tract, metabolic diseases, selected oncological diseases, and diseases of the immune system) will be studied.
The aim of the molecular-epidemiological study is to study and assess the relations between expositions towards environmental factors, factors of lifestyle, and their impact upon genetic and epigenetic parameters of the medical condition and aging in middle-aged individuals (miRNA, middle telomere length).
The socioeconomic study will be dealing with evaluation of perception of environmental risk factors, lifestyle factors, and psychosocial factors in relation to health and healthy aging of middle-aged individuals, including the cohort of mothers, municipal police officers and runners, using
a socioeconomic questionnaire.
Within the activity of determining the influence of polluted air upon the health of citizens, especially long-term exposition towards pollutants in the air will be evaluated; this activity will be supplemented with a collection of samples of airborne particles and evaluation of short-term exposition in the cohorts of runners and municipal police officers.
Programme 2: Molecular-epidemiological study evaluating the impact of polluted environment upon the genome in new-borns, mothers, municipal police officers, and runners.
Principle investigator: Institute of Experimental Medicine, Czech Academy of Sciences, Department of Genetic Toxicology and Nanotoxicology
The molecular-epidemiological study includes also assessment of the influence of polluted environment upon the genome in new-borns, mothers, municipal police officers, and runners. Specifically, methylation of DNA and expression of selected genes will be studied, together with the study of peroxidation of lipids, formation of DNA adducts, oxidative DNA damage, study of exposition towards persistent contaminants and concentrations of PAU metabolites, study of lipodome, antioxidative activity and immunity markers, and study of morbidity in children below 2 years of age. The reprotoxicity study will be dealing with the relations among biomarkers of genetic damage, oxidative damage and sperm damage in the industrial and control localities. In the study of runners, the researchers will observe the influence of the runners’ load in the industrial and control localities upon the miRNA levels and oxidative damage.
Programme 3: Reprotoxicity study (monitoring of changes in somatic and reproductive cells)
Principle investigator: Veterinary Research Institute, Department of Genetics and Reproduction
The results obtained so far in the past years in a group of municipal police officers in Prague suggest that certain changes in the genetic material in somatic (peripheral lymphocytes) and reproductive (sperm) cells occur. It is necessary to find out how these, and also other, changes are conditioned with a long-term stay in an industrial region with increased environmental pollution, when compared with a locality with a lower load, and various expositions throughout the year. The reprotoxicity study will be mainly studying the relation between polluted environment and the quality of sperm, including determination of chromatin integrity and the degree of DNA methylation in the sperm.
Programme 4: Study of physical activity
Principle investigator: Human Motion Diagnostic Centre, Faculty of Education, University of Ostrava
The study of physical activity attempts to find relations among physical activity, other environmental factors, and the level of environmental pollution, especially in relation to the incidence of running injuries, health, psychological well being, and quality of life. The aim of individual substudies will be to determine the influence of polluted environment and interaction with external environment and biomechanical, physiological, and psychosocial factors upon the incidence of running injuries, selected health indicators, psychical well-being, and the quality of life. Programme 4 consists of two groups of probands (individuals, who will be studied), i.e. physically active, referred to as “runners”, and less physically active, referred to as “non-runners”. The study subjects will be adult males and females of all age categories from the Moravian-Silesian and South Bohemian Regions.